What is RFID?
RFID is the abbreviation of Radio Frequency Identification, which is radio frequency identification, commonly known as electronic label.
What is RFID technology?
RFID radio frequency identification is a non-contact automatic identification technology. It automatically recognizes the target object and acquires relevant data through the radio frequency signal. The identification work can work in various harsh environments without manual intervention. RFID technology can recognize high-speed moving objects and recognize multiple labels at the same time, which is quick and easy to operate.
RFID is a simple wireless system with only two basic components for controlling, detecting, and tracking objects. The system consists of an interrogator (or reader) and a number of transponders (or tags).
Classification of RFID
RFID is divided into low frequency (LF), high frequency (HF), ultra high frequency (UHF), and microwave (MW) according to the application frequency. The corresponding representative frequencies are: low frequency 135KHz, high frequency 13.56MHz, super High frequency 860M~960MHz, microwave 2.4G, 5.8G.
RFID is divided into passive RFID, active RFID, and semi-active RFID according to the way energy is supplied. Passive RFID read and write distance is near, the price is low; active RFID can provide farther read and write distance, but need battery power, the cost is higher, suitable for long-distance reading and writing applications.
What is the basic component of RFID?
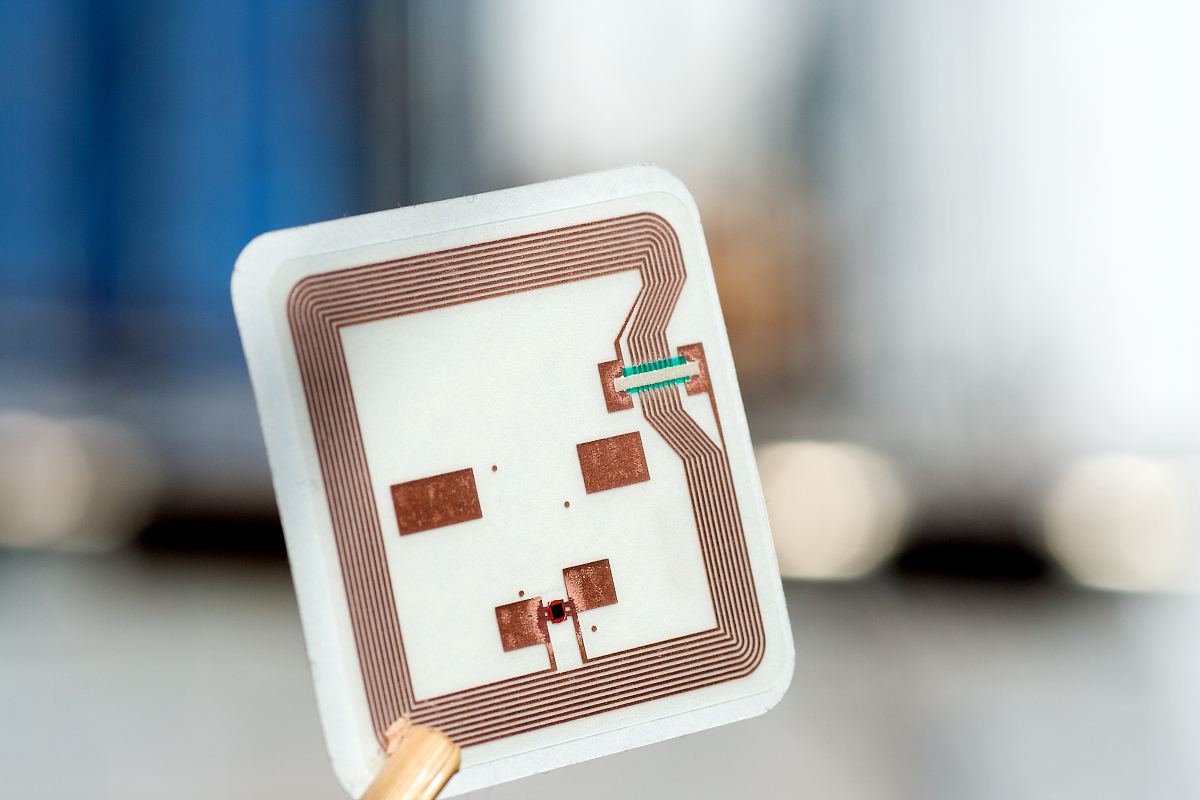
Tag: consists of a coupling element and a chip, each tag having a unique electronic code attached to the object to identify the target object;
Reader: A device that reads (and sometimes writes) tag information and can be designed to be handheld or fixed;
Antenna: Transmits RF signals between the tag and the reader.
What is the basic component of RFID?
Tag: consists of a coupling element and a chip, each tag having a unique electronic code attached to the object to identify the target object;
Reader: A device that reads (and sometimes writes) tag information and can be designed to be handheld or fixed;
Antenna: Transmits RF signals between the tag and the reader.
What is the basic working principle of RFID technology?
The basic working principle of RFID technology is not complicated: after the tag enters the magnetic field, it receives the RF signal from the reader, and sends the product information (passive tag, passive tag or passive tag) stored in the chip by the energy obtained by the induced current. Or actively send a signal of a certain frequency (Active Tag, active tag or active tag); the reader reads the information and decodes it, and sends it to the central information system for data processing.
A complete RFID system consists of a reader (Reader) and an electronic tag (TAG), a so-called transponder and application software system. The working principle is that the reader emits a specific frequency. The radio wave energy is sent to the Transponder to drive the Transponder circuit to send the internal data. At this time, the Reader receives the interpretation data in sequence and sends it to the application for corresponding processing.
In terms of communication and energy sensing between the RFID card reader and the electronic tag, it can be roughly divided into two types: Inductive Coupling and Backscatter Coupling. Generally, low-frequency RFID adopts the first type. Most of the higher frequencies use the second method.
The reader can be a read or read/write device depending on the structure and technology used, and is an RFID system information control and processing center. The reader usually consists of a coupling module, a transceiver module, a control module, and an interface unit. The half-duplex communication is generally used for information exchange between the reader and the transponder, while the reader provides energy and timing by coupling to the passive transponder. In practical applications, management functions such as collection, processing, and remote transmission of object identification information can be further implemented through Ethernet or WLAN. The transponder is the information carrier of the RFID system. Currently, the transponder is mostly composed of a coupling element (coil, microstrip antenna, etc.) and a microchip.
Why do many retailers like RFID technology?
According to STARNFC’s retail analysts, by using RFID, Wal-Mart can save $8.35 billion annually, most of which is due to labor costs that do not require manual inspection of incoming bar codes. While other analysts believe that the $8 billion figure is too optimistic, there is no doubt that RFID can help solve two of the biggest challenges in the retail industry: goods out of stock and wear and tear (products lost due to theft and supply chain disruption) Now, if it is a theft alone, Wal-Mart’s loss will be almost $2 billion a year. If a legitimate company’s turnover can reach this figure, it can rank 694th in the list of the 1000 largest companies in the United States. . Researchers estimate that this RFID technology can help reduce theft and inventory levels by 25%.
What is the typical application of RFID technology?
- Product performance: Since most products cover 868MHz to 915MHz, the requirements for corresponding reading and writing equipment in the system can be reduced, and the sensitivity to frequency deviation is reduced.
- The product complies with: EPC CLASS 1 GEN 2 and ISO18000-6C.
- Professional services: targeted use of the world’s advanced product experience, specific considerations for commonly used products.
- Adaptation areas: logistics and supply management, manufacturing and assembly, air baggage handling, mail, express parcel processing, document tracking, library management animal identification, sports timing, access control, electronic tickets, road automatic charging. Long distance UHF tags to small UHF tags. Can be customized for customers to meet various requirements.
RFID description
Meet international ISO15693, ISO18000-6B, EPC G2 and other standards, using different antenna design and packaging materials can be made into various forms of labels, such as vehicle labels, pallet labels, logistics labels, metal labels, book labels, liquids Labels, personnel access labels, ticket labels, luggage labels, etc. Customers can select or customize the appropriate electronic label as needed.
RFID reading and writing device
RFID can only play its role when there are reading and writing devices. RFID reading and writing devices include RFID readers, RFID reader modules, etc. Currently, YW-201 and YW-601U and YW-601R are relatively high cost-effective on the market. These devices can read or write RFID data and do a good job of encryption. The long distance is WV-CID1500, and the WV-VID1500 can reach 1.5 kilometers.
The impact of metal and liquid environments on RFID
RFID ultra-high frequency (UHF) tags are sensitive to environments such as metal and liquid due to the characteristics of electromagnetic backscatter, which can make passive tags of this working frequency difficult to have metal surfaces. Working in an object or liquid environment, but such problems have been completely solved with the development of technology. For example, STARNFC label company has developed a passive label that can read applications in a metal or liquid environment. Products to facilitate the deployment of RFID in the above environment or application scenarios.
RFID is widely used in RFID cards, and RFID cards have important applications in identity recognition. STARNFC is a professional RFID card supplier, more products: https://www.starnfc.com/shop/